There are many benefits of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) as a business automation technology. In addition to being one of the fastest growing technologies today, RPA guarantees cost savings, is faster than traditional automation, does not demand systems or database integration, and can be configured to an interface with applications used in many business operations.
RPA can perform any rules-based task and provides an audit trail report of processes and transactions executed, which can be used to complement and automate interfaces between ERP, CRM, BPMS and workflow tools. This allows businesses to get immediate ROI. However, for successful results with RPA, feasibility assessment is critical.
Conducting an RPA Feasibility Assessment
Before progressing further on how to conduct RPA feasibility, it's important to understand the process of automation. See the visual below.
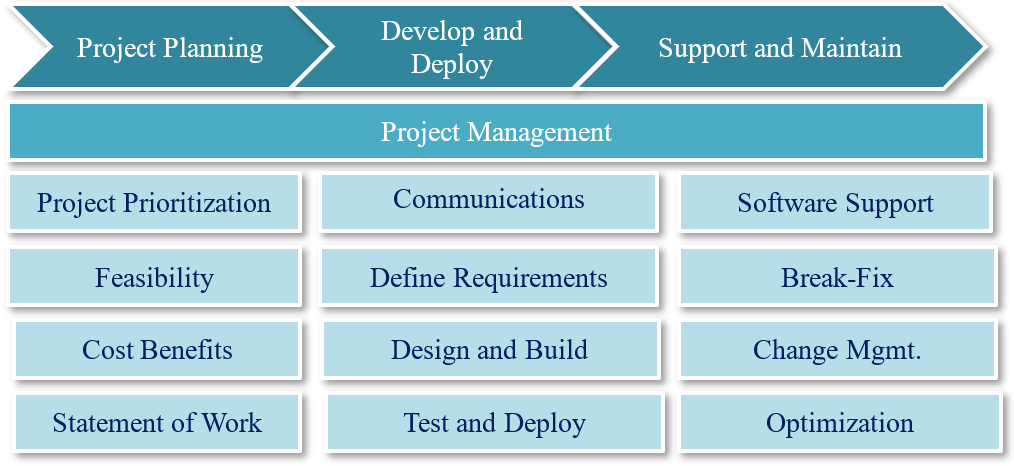
Process feasibility is one of the most vital components of the RPA automation framework. It consists of two steps: process examination and technical feasibility. A few key people are required to conduct the feasibility assessment, including the operation user, an SME (Subject Matter Expert) and an RPA expert.
Stage 1: Process Examination
In this stage, the SME should make a list of the step-by-step process, down to keystroke and mouse click levels. The remaining steps should go as follows:
- Identify the nature of each step and activity performed by the operation user and validate whether the process received the rule-based activity or requires any additional decisions or analysis from the user.
- Ascertain preventive elements that can be automated, then decide on the type of application, followed by downtime, and so on.
- Validate the input data type, structured or unstructured, and template creation or modification.
- Define the process scenarios or sub-scenarios, as well as the need to capture the time taken of each request with the specified scenarios.
Stage 2: Technical Feasibility
The RPA expert should validate the defined logics, rule-based steps, and input & output data, then ensure the process is suitable for automation. Also, mention any manual intervention if needed during the process, followed by complexity analysis, volume of transactions, technology landscape, development efforts, data size and information flow. Additionally, consider the process standardization or do re-engineering if required.
Below are the key components needed to be performed during the feasibility study:
Process Level
- Create a process document that contains the high-level steps or process map.
- Define the most common errors and process flows to fix or escalate these errors.
- Create a business application decision and provide details.
Metrics
- Define schedule details to make sure it follows the standard set timings as per daily, weekly or monthly.
- Define whether the process must be completed by a standard set timing or date.
- Define daily transaction count details.
- Provide average timings per transaction and define how many errors found.
- Mention how long it takes to rectify an error.
Applications & Data
- Provide application details and other prerequisites.
- Mention the input or trigger (Excel spreadsheet, CSV file, email, workflow or time of day) that leads the process and source details.
- Provide output and format details (letter/email to a customer, notification to a service area, spreadsheet or management report).
- Update the test environment that mirrors the live system and mention the access to the same inputs and outputs.
Support
- Provide resource availability details for support throughout the User Acceptance Testing (UAT) and implementation process
- Define Service Level Agreement (SLA) details

.jpg?width=1110&name=RPA%20(2).jpg)














