Automation is the key driver to succeed in the digital transformation journey. To have successful automation, businesses are adopting various automation technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Intelligent Process Automation (IPA), Artificial Intelligence (AI) and so on. A lot of comparisons have been drawn between RPA and IPA and businesses are confused on which to implement for their needs. Here we discuss the key differences between RPA and IPA.
The Differences Between RPA and IPA
Though RPA and IPA appear similar, the functionality and scale of automation differ significantly. RPA analyzes a substantial amount of enterprise or process data to trigger a new activity, sends out replies, and interact with other business systems. These are completely rule-based bots, that automate repetitive business tasks. No decisions or intelligence is involved in RPA.
RPA bots complete fundamental tasks that don’t need deep insights. Instead, RPA handles routine and some limited computational tasks. Predominantly, the idea of RPA is to run what the developer code has directed and depends on human supervision. The goal of adding IPA is to enable the RPA robots to discover, think, and learn for themselves.
IPA powered by intelligent technologies like machine learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and AI, use knowledge-based workflows to automate various business functions and processes. These applications learn, evolve, and continuously improve over time. IPA streamlines business processes and drives complicated decisions quickly, while enabling businesses to discover, model, evaluate, calculate, augment, optimize, manage, and automate various functions to increase productivity and efficacy.
IPA-based automation bots improve current processes automatically by learning from previous execution data and from other trained data sets. The beauty of IPA technology is it can effectively process structured and partially structured data of different formats and drive intelligent decisions.
IPA ensures the quality of business process execution and performance at reduced costs. In IPA, artificial intelligence is used to build new procedures for ML algorithms to achieve learning. IPA is used for end-to-end automation of convoluted business processes.

The key difference between RPA and IPA is, RPA is rule-based automation. However, business processes often operate beyond predefined rule sets which drives the need for cognitive abilities to make decisions. Not all business process automation demands intelligence and can operate on predefined repetitive tasks without any deviation, here RPA excels. But if the requirement demands higher decision-making capabilities, in such cases IPA is the appropriate choice.
RPA automation solely relies on the data supplied and if the sourced data is biased then the results will be inaccurate. So, with RPA it is critical to verify data. Here IPA uses the AI tools to analyze unstructured data of various formats then cleans and prepares the data. Here businesses can define parameters to clean the data. To obtain data accuracy, businesses can also integrate RPA and AI to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of automation efforts.
Analyzing IPA Market Value
Looking at these immense capabilities, IPA adoption is growing rapidly by businesses across the globe that anticipate, slashing operating costs.
Even though the market valuation of IPA hasn’t matched up to the RPA market, IPA has matured over time and is anticipated to continue to grow in popularity.
As per Statista research findings on IPA and RPA, it's projected that $10.9 billion will be spent on IPA whereas the RPA and AI business operations are likely to have a less expenditure with $5.4 and $4 billion respectively.
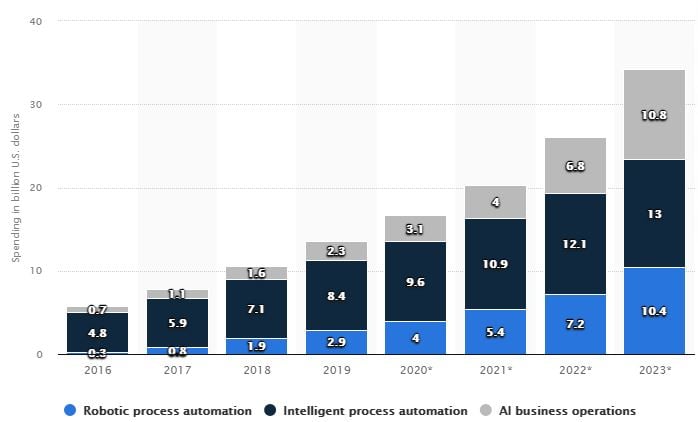
Report Linker estimates that the "Global Intelligent Process Automation Market size is expected to reach $15.8 billion by 2025, rising at a market growth of 12.5% during the forecast period”. Another report of Markets and Markets research valued the IPA market at $6.25 billion in 2017 and is expects it to be $13.75 billion by 2023.
Conclusion
While some may say IPA will be the end of RPA, these discussions are purely illogical as each has its own specific use cases and capabilities. Moreover, businesses are developing strategies that combine RPA and IPA capabilities. Businesses can consider an integrated RPA and IPA approach to achieve better automation results.
















