The software testing industry has been working hard to sort out ways for optimizing the amount of effort, cost and time in the overall process. Streamlining data testing and management plays an equally important role in the Quality Assurance (QA) process and in end-user and customer's perspectives. Test Data Management is critical in the project development life cycle and to maintain the quality of the product’s deliverables.
What is Test Data?
For our test applications, we cannot provide real time data, and if we use realistic data, it might lead to conflict in the production environment.
Whenever we want to perform Quality Assurance activities on any application, we need to enter valid details for that application. With this approach, we can complete testing for most of the features. Always, for better usage, QA needs to save the data somewhere in order to use it for the next time. That set of data can be reused whenever required and this set of identified data that can be utilized in further testing is nothing but “Test Data”.
In simple words, Test Data is nothing but the details that we provide in our application in order to test it. In every project or in any company, the test data is stored or saved in excel sheets so that QA teams can utilize it for the manual execution or use it for conducting automation tests, which will be useful for future references.
Benefits of Test Data Management
- Always makes a note of test data that is utilized for testing a particular scenario
- This coverage can be done in both positive and negative test cases
- Track the test data and segregate them separately for the positive and negative test cases
- Most of the complex applications need a wide range of test data that should be saved with the QA team and utilize it in the proper channels inappropriate manner
- Always note down what kind of test data you require before you start testing the application. Example: If you are performing your QA activities in the Banking domain of a particular country, we need to request the valid data from the bureau team officially so that, the CIBIL score would be appropriate
- Never misuse the test data in any kind of illegal activity
- Do not create any sort of disturbance by using your friend’s email ID’s, Mobile numbers. Some applications will generate emails/ alerts to the provided details. It might irritate your people
Who Manages the Test Data?
Test data is managed through the test data management tool. This tool separates a wide range of data that can be used for testing from the real-world data or production data.
Test data management tools generally follow these steps to produce test data:
- Test data of different formats are saved in a particular location.
- The tool extracts the data set from the provided location.
- After extracting the data set, the tool will separate client-related data.
- The tool will compare the actual data with test data in order to check the accuracy of the application.
- In order to maintain this data set in the future, the tool refreshes the test data as per the need.
Some of the popular test data management tools are:
- Informatica
- CA Test Data Manager (Datamaker)
- Optim
- LISA Solutions
- DATPROF – Test Data Simplified
- SAP Test Data Migration Server
Test Data Management Strategies
There are 4 factors to utilize for valid test data. They are:
- Exploring test data
- Validating test data
- Building test data for re-usability
- Automating TDM tasks to accelerate the process
Types of Test Data Useful for Different Applications
Test Data can be in any format. Most of the data will be tracked in Excel sheets and generally be saved in the shared folders of a particular project. The test data saved will be valuable in one or the other way. Different applications such as Pharma, Healthcare, Aviation and BFSI have their own requirements in utilizing test data per the project’s need.
Test Data can be managed or identified and further organized with multiple factors such as:
- Test- Specific Data: This type of data is useful only for particular reusable scenarios.
- Test -Reference Data: To check the test performance we store this kind of data. If the user data is relevant it can be noted that it has influence in order to complete test scenarios. For example: If a system has to depend on any third-party intervention to get the result we use this kind of data. Most commonly used would be for FICO or CIBIL score calculations.
- Application Reference Data: It is irrelevant or not dependent on strategic approaches under test. This kind of data is required to start the application testing.
Test Data Types
- Wrong Data: QA should be careful while entering data to test the system for a positive approach. If you are performing negative testing, QA can practice wrong data submission.
- Invalid Test Data: QA should identify the approach they are using and accordingly we need to pick the data. With this invalid test data QA can get to know whether the system is displaying relevant error messages or not.
- Boundary Test Data: Considering boundary values QA needs to perform testing using a set of test data.
- Valid Test Data: Valid test data is useful for the positive approach for testing an application for desired results.
- Absent Data: Entering blanks in the fields and validating the result is nothing but checking Absent data. This can be tested mostly in form filling applications DB testing with Null Insertion and validating front end result.
Ways to Create the Test Data
- Manually
- Import from the production environment
- Duplication from prior customer systems
- Using automation testing tools
Here is the approach to be used for effective management of test data:
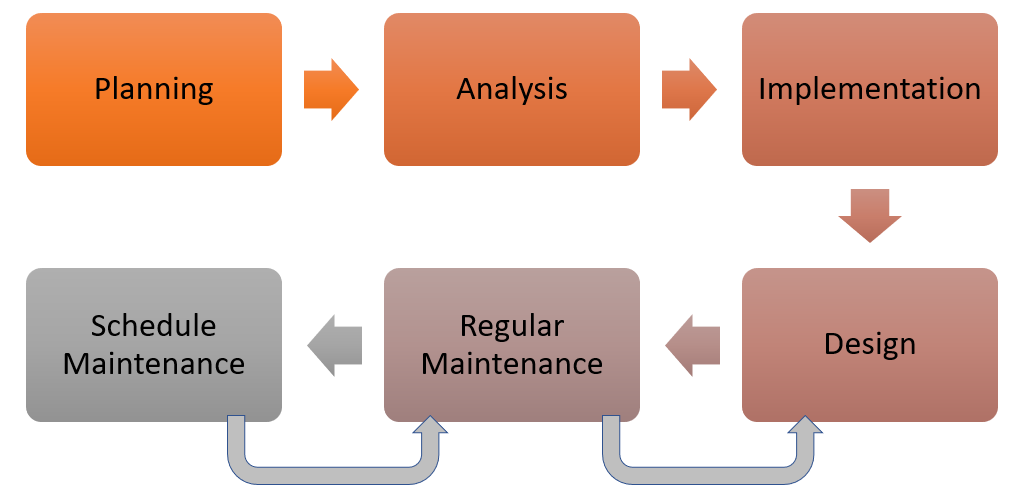
In the legacy model, data was very rarely used because the QA segment is not in high scope. Once the QA standards are recognized the usage of test data became widespread. In order to provide quality outputs, the implementation methods to manage test data became very popular.
Conclusion
For every project, the environment we work should be the main focus. First, identify the test environment, type of scenario and then utilizes the test data effectively. This utilization should be useful for several releases and different cycles of testing.
















